Isomerism in Coordination Compounds
Isomerism in Coordination Compounds: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Optical Isomerism, Geometrical Isomerism, Stereoisomerism, Structural Isomerism, Isomerism in Coordination Compounds, Linkage Isomerism, Coordination Isomerism, Optically Active Compounds and, Ionization Isomerism
Important Questions on Isomerism in Coordination Compounds
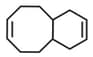
Number of geometrical isomer of given compound will be:
Which of the following compounds does exhibit stereoisomerism?
Identify the isomer occur in the given ligand. _____ (Facial (fac) isomer/ Meridional (mer) isomer)
Define Facial (fac) isomer.
If three donor atoms of the same ligands occupy adjacent positions at the corners of an octahedral face, we have the facial (fac) isomer.
State the method to draw the different geometrical forms for a particular complex in octahedral geometry.
State the method to draw the different geometrical forms for a particular complex in square planer geometry.
_____ planar complexes do not show optical isomerism.
Square planar complexes show optical isomerism.
What is coordination isomerism in coordination compounds ?
What is Structural isomerism How is it classified?
Due to the presence of ambidentate ligands coordination compounds show isomerism. Palladium complexes of the type and are _____(linkage isomers/ionisation isomers)
Draw cis and trans geometrical isomers of .
Give the enantiomers of
Draw the structure of the fac-isomer of
Which of the following complexes exhibit optical isomerism?
Which of the following is a type of structural isomerism?
The isomerism exhibited by the coordination compounds shown below is:
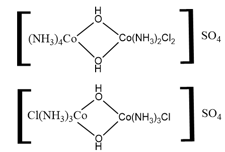
The compounds shown below exhibit _____ isomerism.
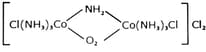 and
and 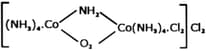
The isomerism exhibited by polynuclear coordination compounds having same molecular formula, same number of coordinating groups and are differently oriented around the central metal ion is _____
